Evolution and Impact of Digital Marketing in the Modern Business Landscape
Digital marketing has come a long way since the early days of the Internet. Initially, it consisted of basic online advertising and email marketing.
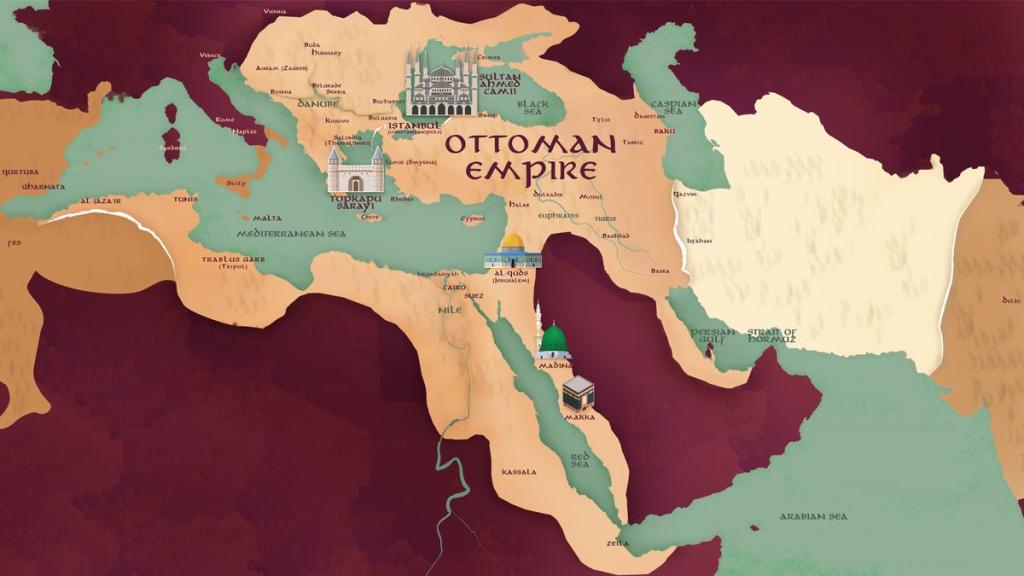
The Ottoman Empire was a powerful and influential empire that played a significant role in world history. Its rise, reign, and fall can be attributed to a variety of factors, including economic, military, and political challenges.
The Ottoman Empire was one of the most powerful and longest-lasting empires in world history. It was founded in 1299 and lasted until the early 20th century. The empire was known for its military prowess, cultural achievements, and vast territories. In this article, we will delve into the history of the Ottoman Empire and explore its rise, reign, and fall.
Table of contents [Show]
The Ottoman Empire was founded in 1299 by Osman I, a leader of the Turkish tribes in Anatolia.
The Ottoman Empire expanded its territory through military conquests and diplomacy. They defeated the Byzantine Empire gained control of much of Anatolia, and then went on to conquer the Balkans, Egypt, and the Middle East.
The head of the Ottoman Empire was the sultan, who held both political and religious power. The first sultan was Osman I, who founded the empire in 1299.
The sultan was chosen from among the male members of the ruling dynasty, known as the Ottoman House. The sultan was usually chosen by the previous sultan, who would select his son or another close relative as his successor.
The Ottoman Empire ruled its territories through a system of provinces called vilayets, each governed by a bey, or governor. The empire was also divided into smaller administrative units called sanjaks, which were governed by a sanjak bey. The sultan had ultimate authority over all of these officials, and the empire also had a powerful military that helped to maintain control over its territories.
The Ottoman Empire was a monarchy, with the sultan as the head of state. The empire had a complex system of government, with the sultan at the top, followed by the Grand Vizier and other high officials, and then the beys and sanjak beys who governed the provinces and smaller administrative units. The empire also had a powerful military and a system of law, which helped to maintain order and stability.
The Ottoman Empire was known for its military prowess, cultural achievements, and architectural masterpieces. The empire was also known for its art, literature, and music, and it had a rich tradition of poetry, calligraphy, and miniature painting. The empire also had a strong legal system, which was based on Islamic law, and it had a well-educated and cultured elite
The Ottoman Empire managed its internal affairs through a complex system of government, which was divided into different levels and branches. The empire had a central government, which was headed by the sultan, and it also had local and regional governments, which were headed by the Beys and Sanjak Beys. The empire also had a powerful military, which helped to maintain order and stability, and it had a legal system, which was based on Islamic law.
The end of the Ottoman Empire was brought about by a combination of factors, including economic, military, and political challenges. The empire had been in decline for several centuries, but the final blow came during World War I. The Ottoman Empire, along with Germany and Austria-Hungary, was on the side of the Central Powers, while the Allies included France, Great Britain, Russia, and later, the United States. The Ottoman Empire's defeat in World War I was a major factor in the end of the empire.
The war ended with the signing of the Treaty of Sèvres on August 10, 1920, which imposed harsh terms on the Ottoman Empire, including the loss of territory and the imposition of heavy reparations. However, the treaty was never fully implemented as the newly formed government of the Republic of Turkey, led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, launched a successful War of Independence against the invading Greek army and their allies, which ended with the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne in 1923.
The last war the Ottoman Empire lost was the First World War, where the empire's military was stretched thin by fighting on multiple fronts and was unable to fend off the superior forces of the Allies. Additionally, the empire was also facing internal issues such as economic crisis, political instability, and ethnic tensions which further weakened its ability to fight the war. The defeat in the war and the harsh terms imposed by the Treaty of Sèvres dealt a fatal blow to the empire and led to its eventual demise.
The Ottoman Empire was a powerful and influential empire that played a significant role in world history. Its rise, reign, and fall can be attributed to a variety of factors, including economic, military, and political challenges. The empire left a lasting impact on the world through its military conquests, cultural achievements, and architectural masterpieces. Although the empire is no longer in existence, its legacy continues to be felt today in the countries that were once under its rule.
Digital marketing has come a long way since the early days of the Internet. Initially, it consisted of basic online advertising and email marketing.
Imagery is a dynamic and influential medium that permeates every aspect of our visual culture. From the early days of print to the digital age, artists are pushing boundaries, blending art and technology to create amazing visual statements...
Imagine a world where the air crackles with electricity, where the clash of elements creates a symphony of power. Thundering and lightning, the dynamic duo of the sky, come together in a breathtaking display of nature's might.

